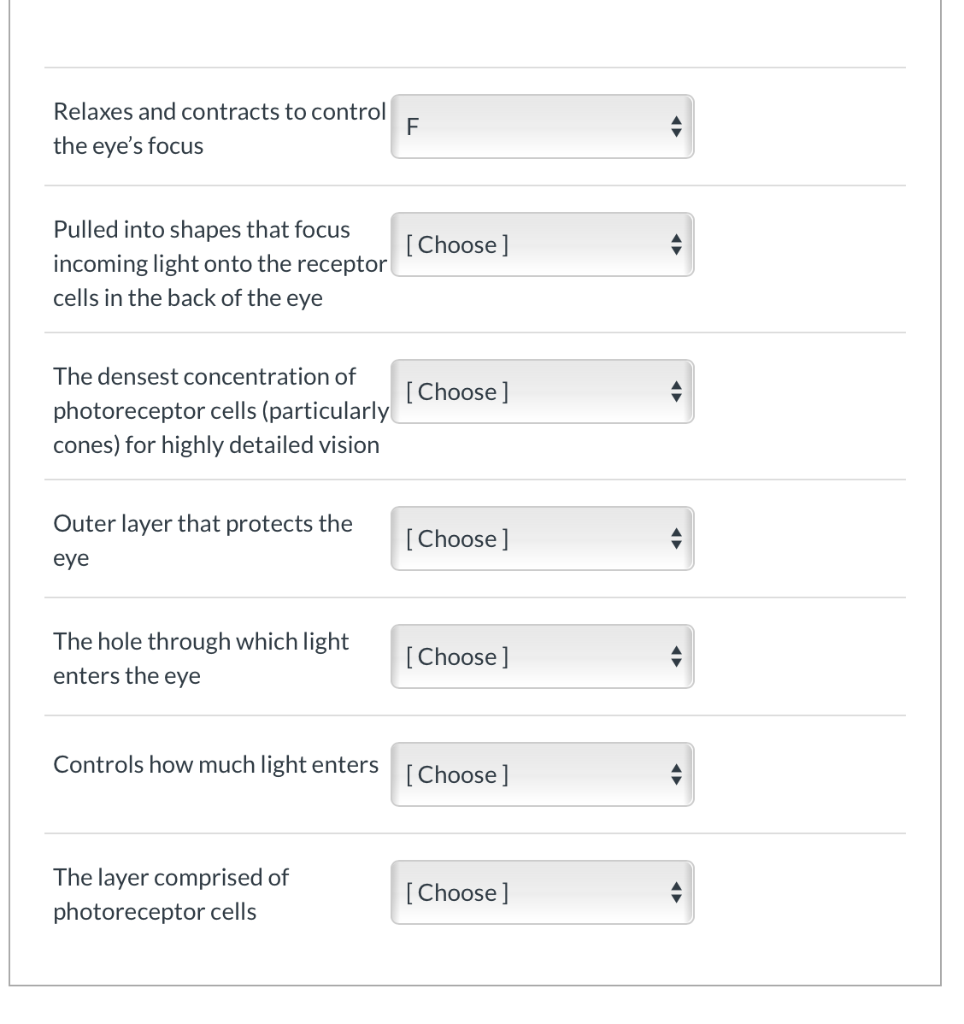
Your Relaxes and contracts to control the eyes focus images are available in this site. Relaxes and contracts to control the eyes focus are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Relaxes and contracts to control the eyes focus files here. Get all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re looking for relaxes and contracts to control the eyes focus pictures information related to the relaxes and contracts to control the eyes focus keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our website always provides you with suggestions for seeing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video articles and graphics that match your interests.
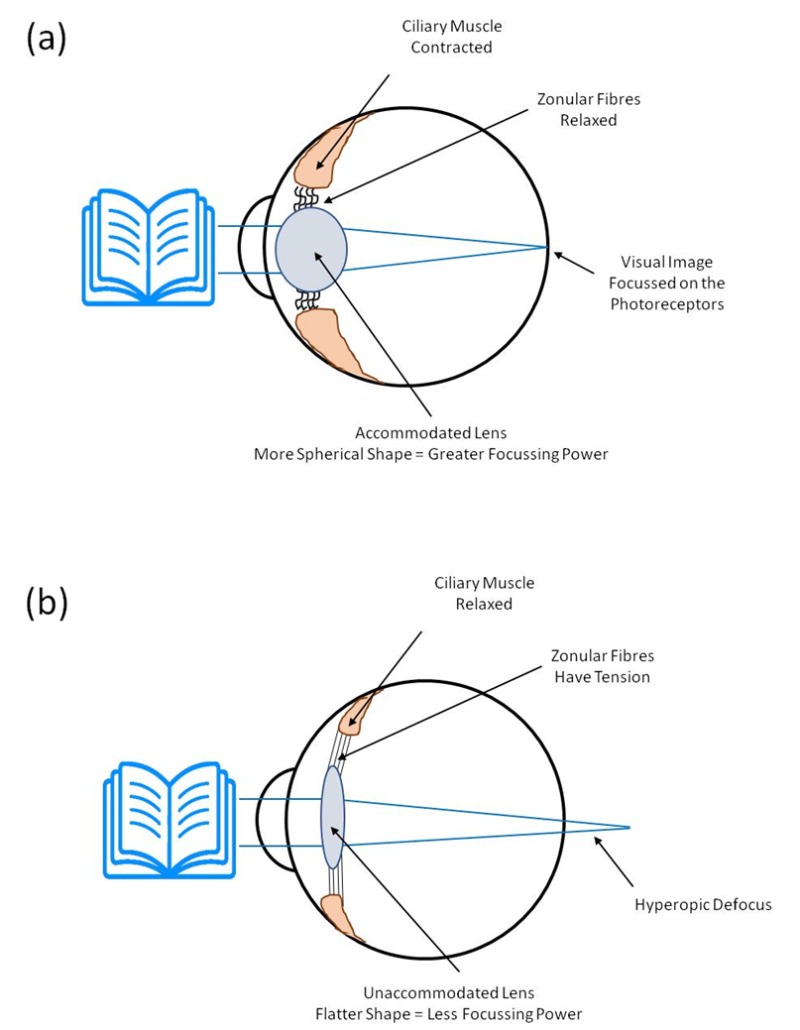
Relaxes And Contracts To Control The Eyes Focus. Lenses move forward or backward to control. Contains light sensitive receptor cells. The lens becomes more convex generally improving the focus for closer objects. The ciliary muscle contracts to release tension on the lens which relaxes into a thicker more spherical shape to focus on nearer objects.
 Yoga Script For Focusing On Breath To Produce Calmness Guided Meditation Scripts Meditation Scripts Yoga Nidra Script From pinterest.com
Yoga Script For Focusing On Breath To Produce Calmness Guided Meditation Scripts Meditation Scripts Yoga Nidra Script From pinterest.com
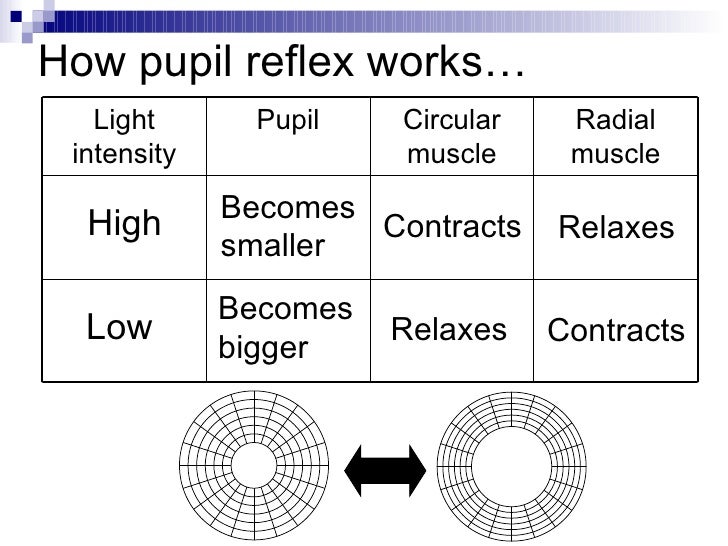
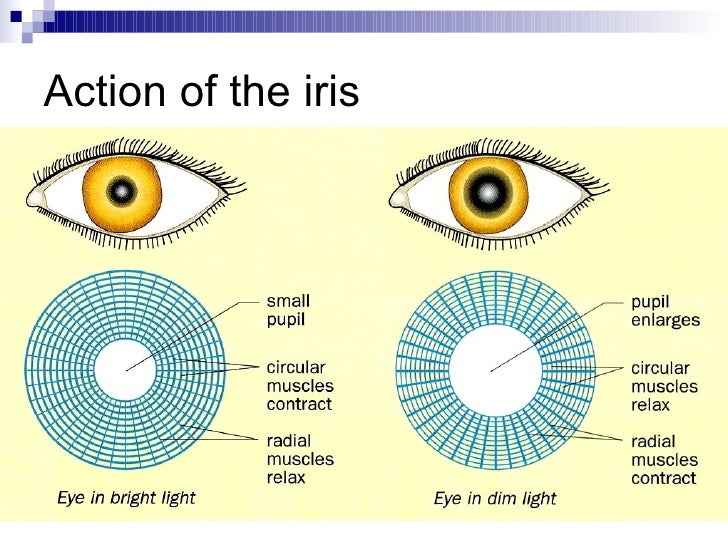
Lens becomes more spherical There are hundreds of primary taste gustation sensations. Allows for details give color. It is actually a circular muscle that contracts or relaxes depending on the amount of light it senses. The outer layer that protects the eye and focuses light onto the lens. The iris serves as the aperture stop for the eye closing to about 2mm in diameter in bright light and opening to a maximum of about 8mm. Relaxes and contracts to control the eyes focal distance.
When the ciliary muscles in the human eye contract.
Relaxes and contracts to control the eyes focal distance. Retina The lining of the back of eye containing two types of light receptor cells. Focusing for near vision - circular muscle contracts - more convex - diverging rays. Relaxes and contracts to control the eyes focal distance. This portion of the eye is what controls the amount of light that is let into the inner eye. This allows control of aberration caused by changes in the focal length of the focus variable lens.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Pulled into shapes that focus incoming light onto the receptor cells in the back of the eye. When it relaxes it flattens the lens generally improving the focus for farther objects. The lens becomes more flat generally improving the focus for closer objects. The area with the densest concentration of photoreceptor cells that allows us to see in great detail. Pulled into shapes that focus incoming light onto the receptor cells in the back of the eye.
 Source: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Source: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
This portion of the eye is what controls the amount of light that is let into the inner eye. Lens becomes more spherical There are hundreds of primary taste gustation sensations. Focusing for near vision - circular muscle contracts - more convex - diverging rays. The area with the densest concentration of photoreceptor cells that allows us to see in great detail. Contracts and relaxes to change the shape of lens coloured muscular part of the eye that eye controls the pupils opening in the iris that lets light through to the retina Transparent front part of the eye that refracts light.
 Source: newhorizonsvisiontherapy.com
Source: newhorizonsvisiontherapy.com
Relaxes and contracts to control the eyes focal distance. The color of the iris is due to various pigmented cells incorporated into the. Relaxes and contracts to control the eyes focal distance. The iris serves as the aperture stop for the eye closing to about 2mm in diameter in bright light and opening to a maximum of about 8mm. The outer layer that protects the eye and focuses light onto the lens.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The ciliary muscle contracts to release tension on the lens which relaxes into a thicker more spherical shape to focus on nearer objects. When the ciliary body contracts the suspensory ligaments relax. It is actually a circular muscle that contracts or relaxes depending on the amount of light it senses. It also keeps the retina against the wall of the eye. The iris relaxes and contracts to protect the retina from excess light.
 Source: ar.pinterest.com
Source: ar.pinterest.com
This portion of the eye is what controls the amount of light that is let into the inner eye. When it relaxes it flattens the lens generally improving the focus for farther objects. Focusing for near vision - circular muscle contracts - more convex - diverging rays. This allows the lens to thicken increasing the eyes ability to focus up close. Slacken or stretch as the ciliary muscles contract or relax to adjust the thickness and curvature of the lens.
 Source: docbrown.info
Source: docbrown.info
Relaxes and contracts to control the eyes focal distance. Relaxes and contracts to control the eyes focal distance. The lens becomes more convex generally improving the focus for farther objects. When it relaxes it flattens the lens generally improving the focus for farther objects. The area with the densest concentration of photoreceptor cells that allows us to see in great detail.
 Source: uilis.unsyiah.ac.id
Source: uilis.unsyiah.ac.id
The area with the densest concentration of photoreceptor cells that allows us to see in great detail. Lenses move forward or backward to control. The lens becomes more convex generally improving the focus for farther objects. Lens becomes more spherical There are hundreds of primary taste gustation sensations. Pulled into shapes that focus incoming light onto the receptor cells in the back of the eye.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
When the ciliary body contracts the suspensory ligaments relax. Lens becomes more spherical c. The outer layer that protects the eye and focuses light onto the lens. Fluid behind the lens that helps maintain the shape of the eye and lens. When the ciliary muscles contract they loosen the ciliary fibers which are attached to the envelope of the crystalline lensBecause the lens is pliable it relaxes into a more curves shape increasing its refractive power to accommodate for closer viewing.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Relaxes and contracts to control the eyes focal distance. Lenses move forward or backward to control. When the ciliary body contracts the suspensory ligaments relax. It is actually a circular muscle that contracts or relaxes depending on the amount of light it senses. Slacken or stretch as the ciliary muscles contract or relax to adjust the thickness and curvature of the lens.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Allows for details give color. Focusing for near vision - circular muscle contracts - more convex - diverging rays. Fluid behind the lens that helps maintain the shape of the eye and lens. Contains light sensitive receptor cells. Lenses move forward or backward to control.
 Source: savemyexams.co.uk
Source: savemyexams.co.uk
Focusing for near vision - circular muscle contracts - more convex - diverging rays. Relaxes and contracts to control the eyes focal distance. When the ciliary body contracts the suspensory ligaments relax. When looking at a distant object the ciliary body relaxes causing the suspensory ligaments to contract. Ciliary muscles change the shape of the lens to focus both near and distant objects.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Lens becomes more spherical There are hundreds of primary taste gustation sensations. Pulled into shapes that focus incoming light onto the receptor cells in the back of the eye. The lens becomes more convex generally improving the focus for closer objects. The iris serves as the aperture stop for the eye closing to about 2mm in diameter in bright light and opening to a maximum of about 8mm. Lens becomes more spherical c.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Fluid behind the lens that helps maintain the shape of the eye and lens. The iris relaxes and contracts to protect the retina from excess light. The outer layer that protects the eye and focuses light onto the lens. Relaxes and contracts to control the eyes focal distance. When the ciliary muscles in the human eye contract.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Slacken or stretch as the ciliary muscles contract or relax to adjust the thickness and curvature of the lens. Contains light sensitive receptor cells. The color of the iris is due to various pigmented cells incorporated into the. Focusing for near vision - circular muscle contracts - more convex - diverging rays. When it relaxes it flattens the lens generally improving the focus for farther objects.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Focusing for near vision - circular muscle contracts - more convex - diverging rays. When the ciliary muscles contract they loosen the ciliary fibers which are attached to the envelope of the crystalline lensBecause the lens is pliable it relaxes into a more curves shape increasing its refractive power to accommodate for closer viewing. When looking at a distant object the ciliary body relaxes causing the suspensory ligaments to contract. The area with the densest concentration of photoreceptor cells that allows us to see in great detail. The color of the iris is due to various pigmented cells incorporated into the.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
It also keeps the retina against the wall of the eye. Contracts and relaxes to change the shape of lens coloured muscular part of the eye that eye controls the pupils opening in the iris that lets light through to the retina Transparent front part of the eye that refracts light. Lenses move forward or backward to control. Retina The lining of the back of eye containing two types of light receptor cells. Lens becomes more spherical c.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Fluid behind the lens that helps maintain the shape of the eye and lens. As the ciliary body of the eye contracts and relaxes to adjust the thickness of the lens the thickness of the lens surface film can be continuously changed while attracting the lens surface film. When the ciliary muscles in the human eye contract. The area with the densest concentration of photoreceptor cells that allows us to see in great detail. It is actually a circular muscle that contracts or relaxes depending on the amount of light it senses.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The lens becomes more convex generally improving the focus for closer objects. Relaxes and contracts to control the eyes focal distance. The ciliary muscle relaxes to tighten and flatten the lens to focus on farther objects. When the ciliary muscles contract they loosen the ciliary fibers which are attached to the envelope of the crystalline lensBecause the lens is pliable it relaxes into a more curves shape increasing its refractive power to accommodate for closer viewing. When looking at a distant object the ciliary body relaxes causing the suspensory ligaments to contract.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title relaxes and contracts to control the eyes focus by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





