Your Does yeast reproduce sexually or asexually images are available. Does yeast reproduce sexually or asexually are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Does yeast reproduce sexually or asexually files here. Download all free photos and vectors.
If you’re searching for does yeast reproduce sexually or asexually images information linked to the does yeast reproduce sexually or asexually topic, you have pay a visit to the ideal site. Our site always provides you with hints for refferencing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video articles and images that fit your interests.
Does Yeast Reproduce Sexually Or Asexually. During sexual reproduction these two differing haploid strains mate to form a diploid cell. In budding a small daughter cell bud is formed on the parent cell. Yeasts reproduce asexually either by fission or by budding. Depending on this character they are grouped as fission yeasts Schizosaccharomyces and budding yeasts Zygosaccharomyces.
 Reproduction In Yeast Notes Videos Qa And Tests Grade 11 Biology Yeast Kullabs From kullabs.com
Reproduction In Yeast Notes Videos Qa And Tests Grade 11 Biology Yeast Kullabs From kullabs.com
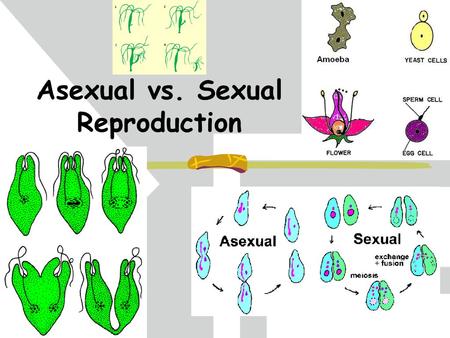
Yeasts undergo both asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction. Yeasts reproduce both sexually and asexually but the latter is more common. Most yeast reproduce asexually. Preparation Task 1 Describe the mechanisms by which meiosis would introduce genetic variability in a population. In the yeast cell cycle cell growth and cell division are tightly linked and are dependent on factors such as nutrient concentration. One type of common yeast is Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Also on the asexual reproduction of yeast the parent cell can divide itself into two cells and develop from there.
Yeasts undergo both asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction. Yeast is a unicellular fungus which reproduces asexually by an unequal division process called budding. Most of the 1500 known species of yeast such as those involved in making breads and wines primarily reproduce asexually through budding. Haploid cells and diploid cells. Yeasts can also reproduce sexually by means of sexual spores called ascospores which result from the fusion of the nuclei from two cells followed by meiosis. Yeasts reproduce asexually by budding or fission.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Depending on environmental cues yeast can undergo asexual or sexual reproduction to produce new cells. Asexual reproduction is a result of mitosis cell division in which the cell simply produces another copy of itself. Yeast can reproduce both as asexually and sexually depending upon the environmental conditions. Yeasts are fungal organisms that can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Yeast reproduces asexually via budding and also reproduces sexually using Asci or Ascospores.
 Source: pediaa.com
Source: pediaa.com
How do yeast reproduce. Yeasts undergo both asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction. The one that undergo asexual reproduction budding is the diploid yeast cell while those reproducing asexually are haploids two mates each containing one copy of the genome. Most yeast reproduce asexually. Haploid yeast cells consist of a single set of homologous chromosomes within the nucleus.
 Source: singerinstruments.com
Source: singerinstruments.com
Asexual reproduction is a result of mitosis cell division in which the cell simply produces another copy of itself. Most of the 1500 known species of yeast such as those involved in making breads and wines primarily reproduce asexually through budding. When this type of yeast reproduces sexually they create spores. Haploid cells and diploid cells. One type of common yeast is Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
 Source: jove.com
Source: jove.com
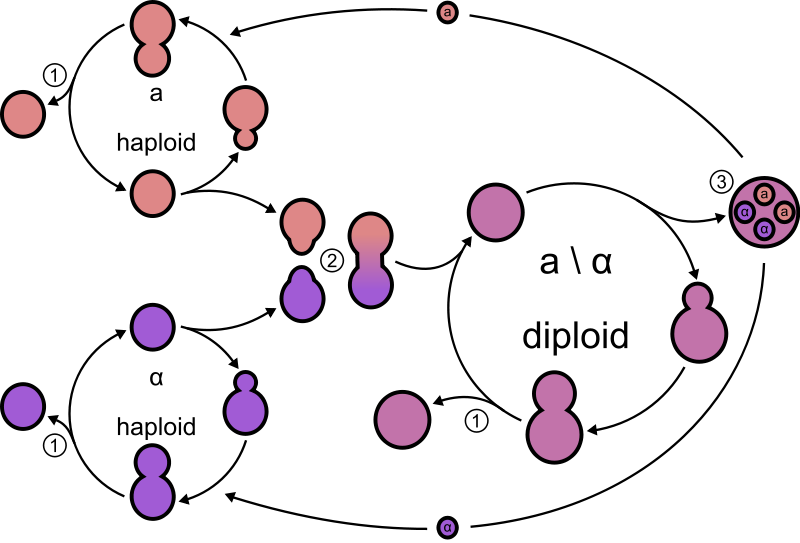
Budding is a type of asexual reproduction in which a. Yeasts undergo both asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction. When using Saccharomyces cerevisiae for brewing or baking the haploid form of the yeast is used. Yeasts reproduce both sexually and asexually but the latter is more common. The two mates are-mate a and mate alpha.
 Source: vedantu.com
Source: vedantu.com
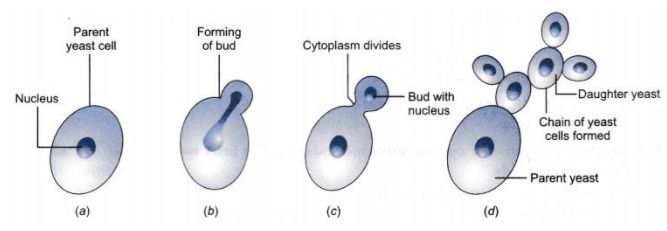
With asexual reproduction the yeast may undergo budding. First it produces a small protuberance on the parent cell that grows to a full size and forms a bud. Yeasts undergo both asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction. Yeast is a unicellular fungus which reproduces asexually by an unequal division process called budding. In budding a small daughter cell bud is formed on the parent cell.
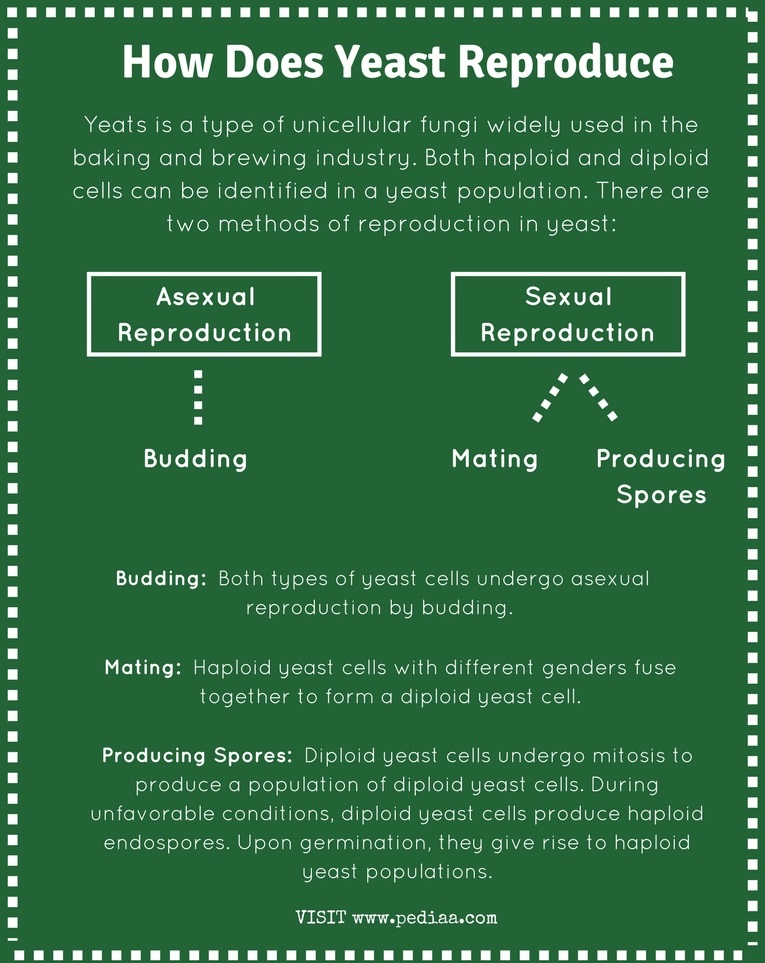 Source: pediaa.com
Source: pediaa.com
Haploid yeast cells consist of a single set of homologous chromosomes within the nucleus. In the yeast cell cycle cell growth and cell division are tightly linked and are dependent on factors such as nutrient concentration. How do yeast reproduce. However diploid yeast cells consist of two sets of homologous chromosomes. Yeasts reproduce asexually by budding or fission.
 Source: brainly.in
Source: brainly.in
Most of the 1500 known species of yeast such as those involved in making breads and wines primarily reproduce asexually through budding. Sexually by producing spores B. Yeast reproduces asexually through budding a small part of the parent cell will bump grow and grow bigger and when it matures it detaches itself and start a new life. When using Saccharomyces cerevisiae for brewing or baking the haploid form of the yeast is used. Haploid cells and diploid cells.
 Source: learn.lif.co.id
Source: learn.lif.co.id
In some circumstances however they may reproduce sexually. Most yeast reproduce asexually. Yeasts reproduce both sexually and asexually but the latter is more common. Yeasts are fungal organisms that can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Preparation Task 1 Describe the mechanisms by which meiosis would introduce genetic variability in a population.
 Source: learn.lif.co.id
Source: learn.lif.co.id
Haploid cells and diploid cells. Most yeasts reproduce asexually by an asymmetric division process called budding. There are two types of cells in a yeast population. Yeasts undergo both asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction. Sexually through binary fission D.
 Source: quora.com
Source: quora.com
Yeasts are fungal organisms that can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Yeasts can also reproduce sexually by means of sexual spores called ascospores which result from the fusion of the nuclei from two cells followed by meiosis. Depending on this character they are grouped as fission yeasts Schizosaccharomyces and budding yeasts Zygosaccharomyces. Sexually through binary fission D. Yeast reproduces asexually through budding a small part of the parent cell will bump grow and grow bigger and when it matures it detaches itself and start a new life.
 Source: yeastsite.wordpress.com
Source: yeastsite.wordpress.com
Asexually by producing spores C. The diploid cell undergoes mitosis to form zygotes. Asexually through binary fission. Sexually through binary fission D. Asexually by producing spores C.
 Source: kullabs.com
Source: kullabs.com
Budding is a type of asexual reproduction in which a. However diploid yeast cells consist of two sets of homologous chromosomes. Haploid cells and diploid cells. Most yeasts reproduce asexually by an asymmetric division process called budding. In budding a small daughter cell bud is formed on the parent cell.
 Source: quora.com
Source: quora.com
When this type of yeast reproduces sexually they create spores. Budding is a type of asexual reproduction in which a. Sexually by producing spores B. Most yeasts reproduce asexually by an asymmetric division process called budding. Depending on this character they are grouped as fission yeasts Schizosaccharomyces and budding yeasts Zygosaccharomyces.
 Source: bioweb.uwlax.edu
Source: bioweb.uwlax.edu
In the yeast cell cycle cell growth and cell division are tightly linked and are dependent on factors such as nutrient concentration. Sexually through binary fission D. The nucleus of the parent cell splits into a daughter nucleus and migrates. To ensure the inhibition of sexual reproduction an isolated form of either haploid is used. Yeasts reproduce asexually by budding or fission.
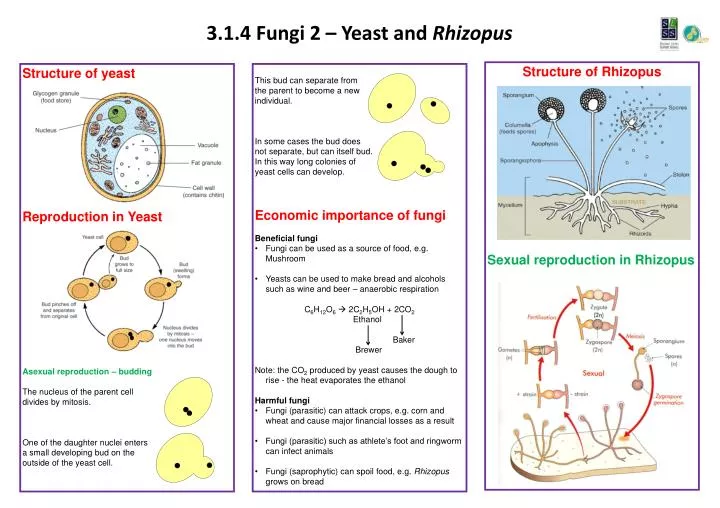 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The two mates are-mate a and mate alpha. When using Saccharomyces cerevisiae for brewing or baking the haploid form of the yeast is used. First it produces a small protuberance on the parent cell that grows to a full size and forms a bud. Yeasts reproduce asexually by budding or fission. During sexual reproduction these two differing haploid strains mate to form a diploid cell.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Yeast have a somewhat unusual ability to reproduce either sexually using meiosis or asexually using mitosis depending on the environment in which they are living. Depending on environmental cues yeast can undergo asexual or sexual reproduction to produce new cells. To ensure the inhibition of sexual reproduction an isolated form of either haploid is used. Yeasts are fungal organisms that can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Yeast can reproduce both as asexually and sexually depending upon the environmental conditions.
 Source: learn.lif.co.id
Source: learn.lif.co.id
In some circumstances however they may reproduce sexually. To ensure the inhibition of sexual reproduction an isolated form of either haploid is used. Yeasts reproduce asexually by budding or fission. Yeast can reproduce both as asexually and sexually depending upon the environmental conditions. Preparation Task 1 Describe the mechanisms by which meiosis would introduce genetic variability in a population.
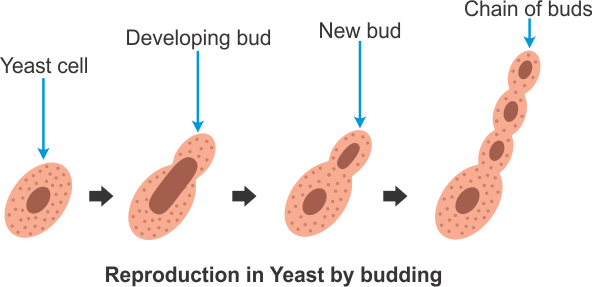 Source: topperlearning.com
Source: topperlearning.com
First it produces a small protuberance on the parent cell that grows to a full size and forms a bud. Budding is a type of asexual reproduction in which a. There are two types of cells in a yeast population. Haploid cells and diploid cells. Yeasts reproduce asexually either by fission or by budding.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title does yeast reproduce sexually or asexually by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.